Online Copper Parts 3D Printing Service
Get precision-crafted copper parts with our online 3D printing service. Specializing in DMLS, SLM, EBM, and LMD processes, we deliver high-quality components using grades like C101, C110, and CuCr1Zr for superior conductivity, strength, and performance.

Send us your designs and specifications for a free quotation
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
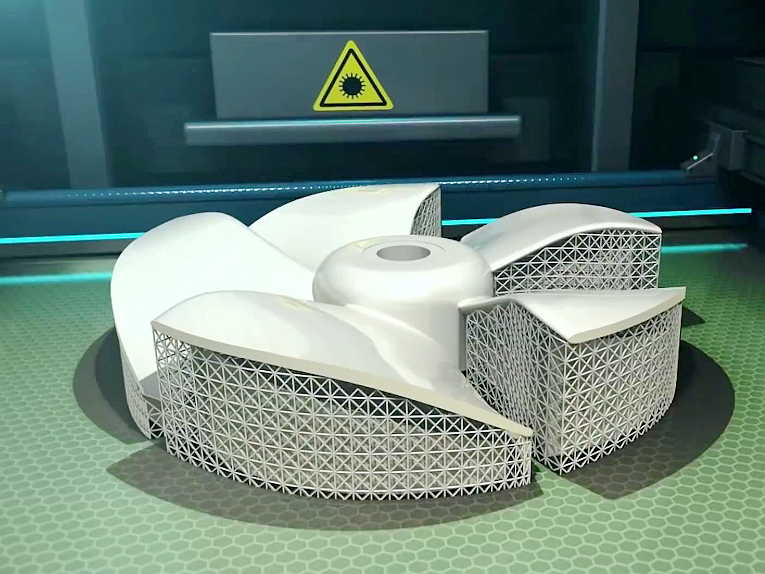
Copper 3D Printing Technologies
Copper 3D printing technologies like DMLS, SLM, EBM, LMD, EBAM, and WAAM offer precision, high conductivity, and strength. These methods ensure dense, high-quality components suitable for complex structures, large-scale parts, and applications demanding superior thermal and electrical properties.
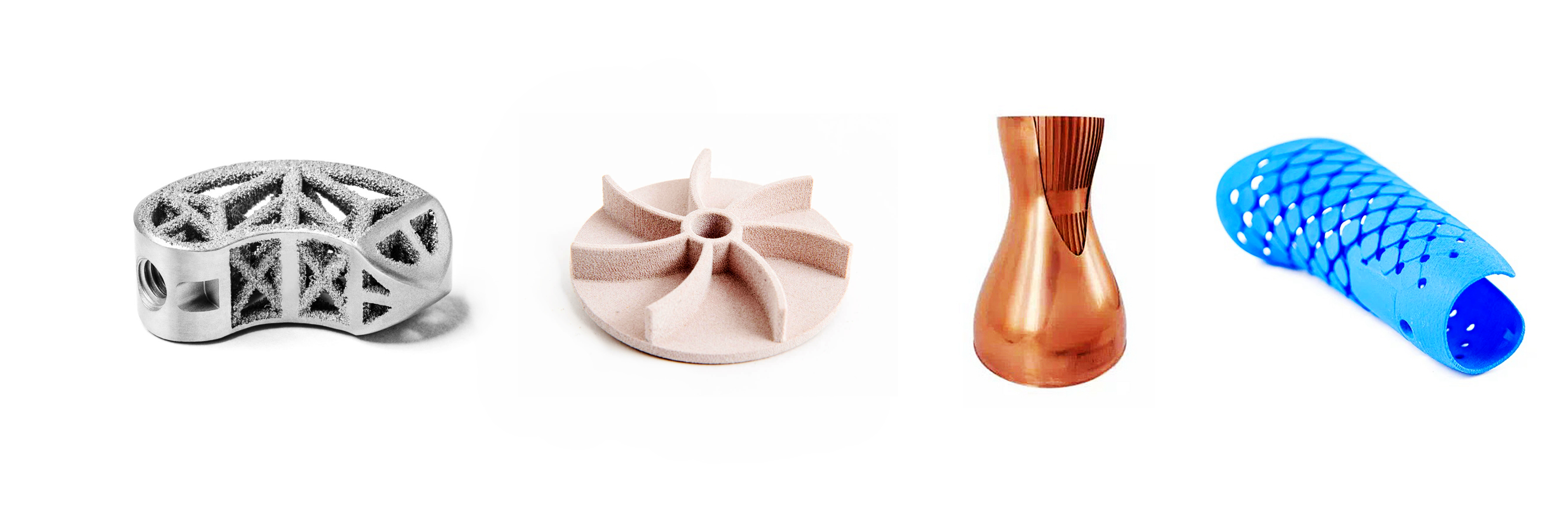
Copper Alloy 3D Printing Materials
Post Process for 3D Printed Copper Parts
Post-processing of 3D-printed copper parts involves methods like CNC machining, EDM, heat treatment, HIP, TBC, and surface treatments. These techniques improve dimensional accuracy, mechanical properties, surface finish, thermal resistance, and durability, ensuring parts meet performance and reliability standards.
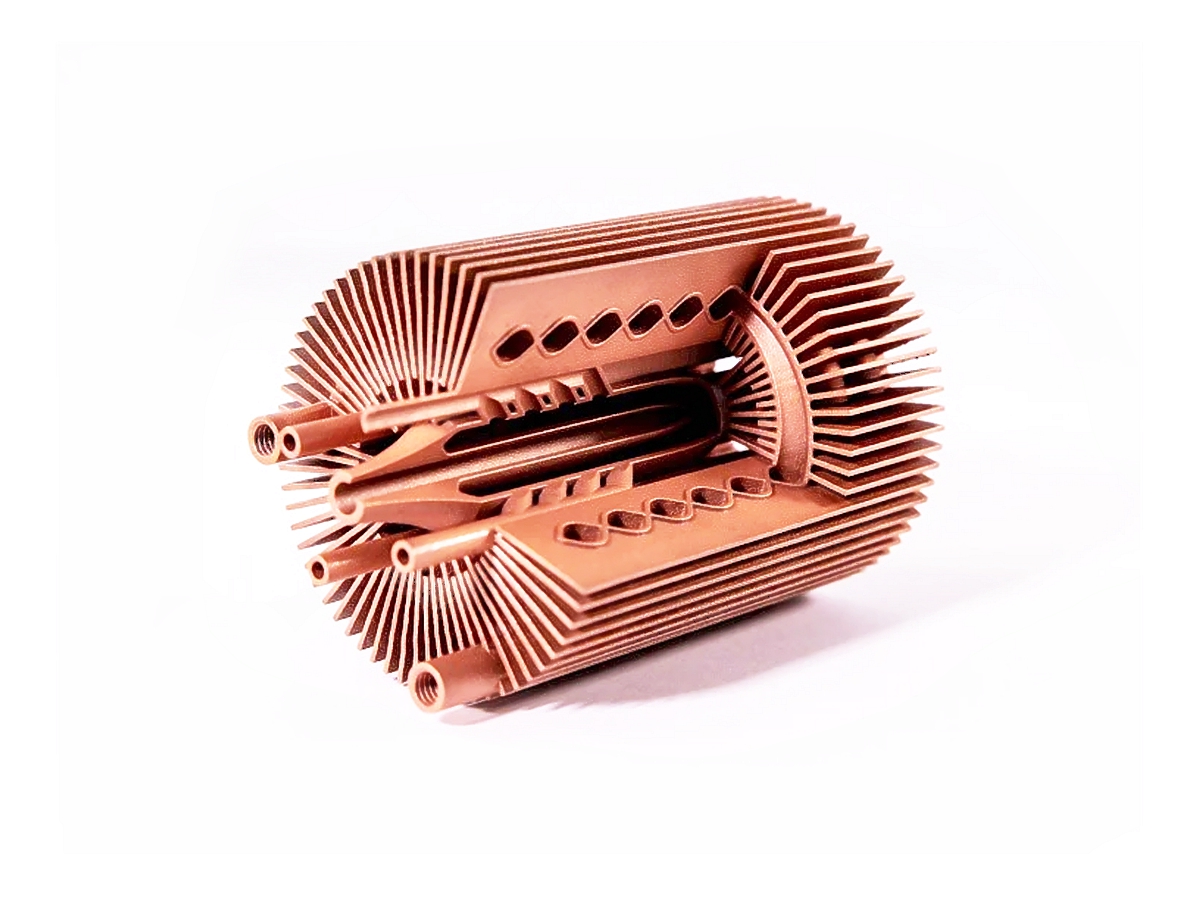
Applications of 3D Printed Copper Parts
3D printed copper parts offer superior thermal and electrical conductivity, making them essential in industries like electronics, energy, and aerospace. These parts are ideal for heat exchangers, electrical components, and cooling systems where efficient heat dissipation and electrical transfer are crucial.
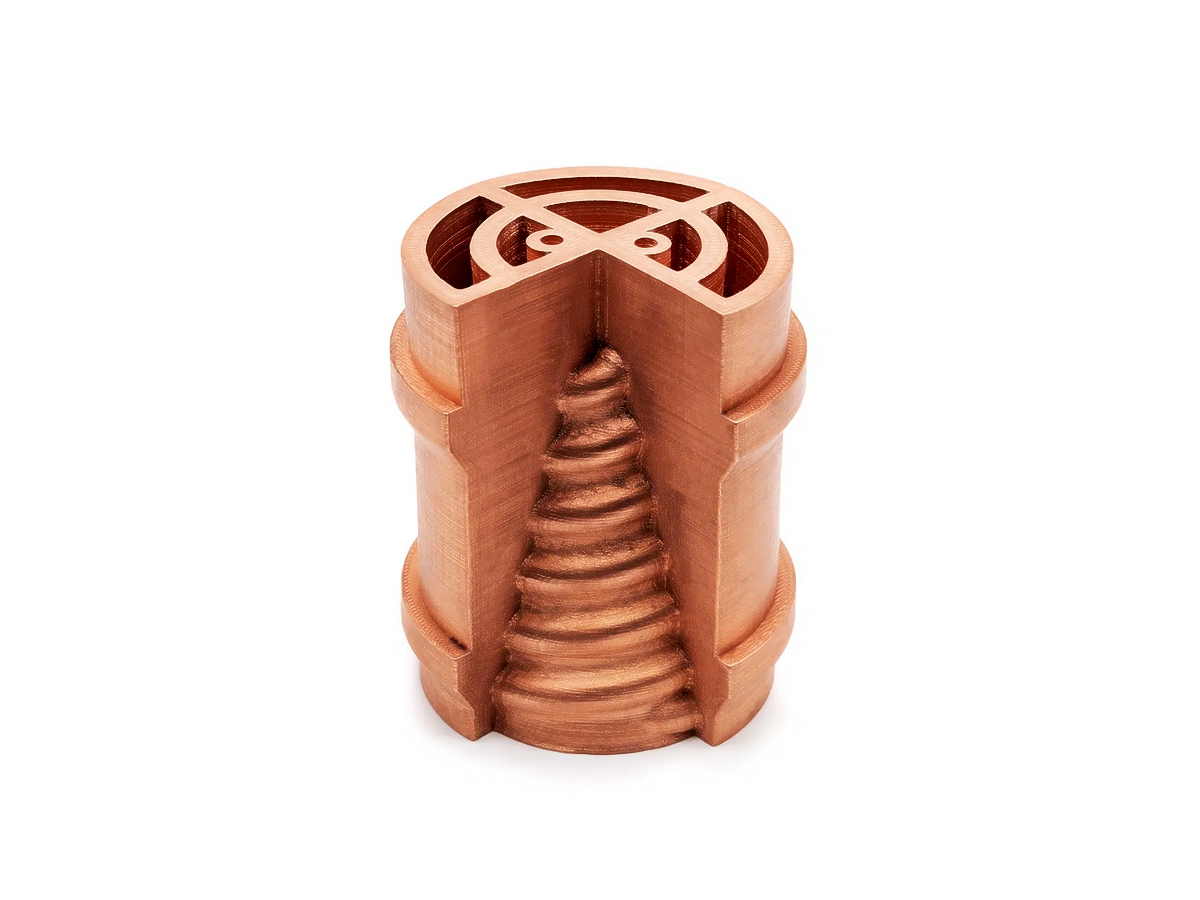
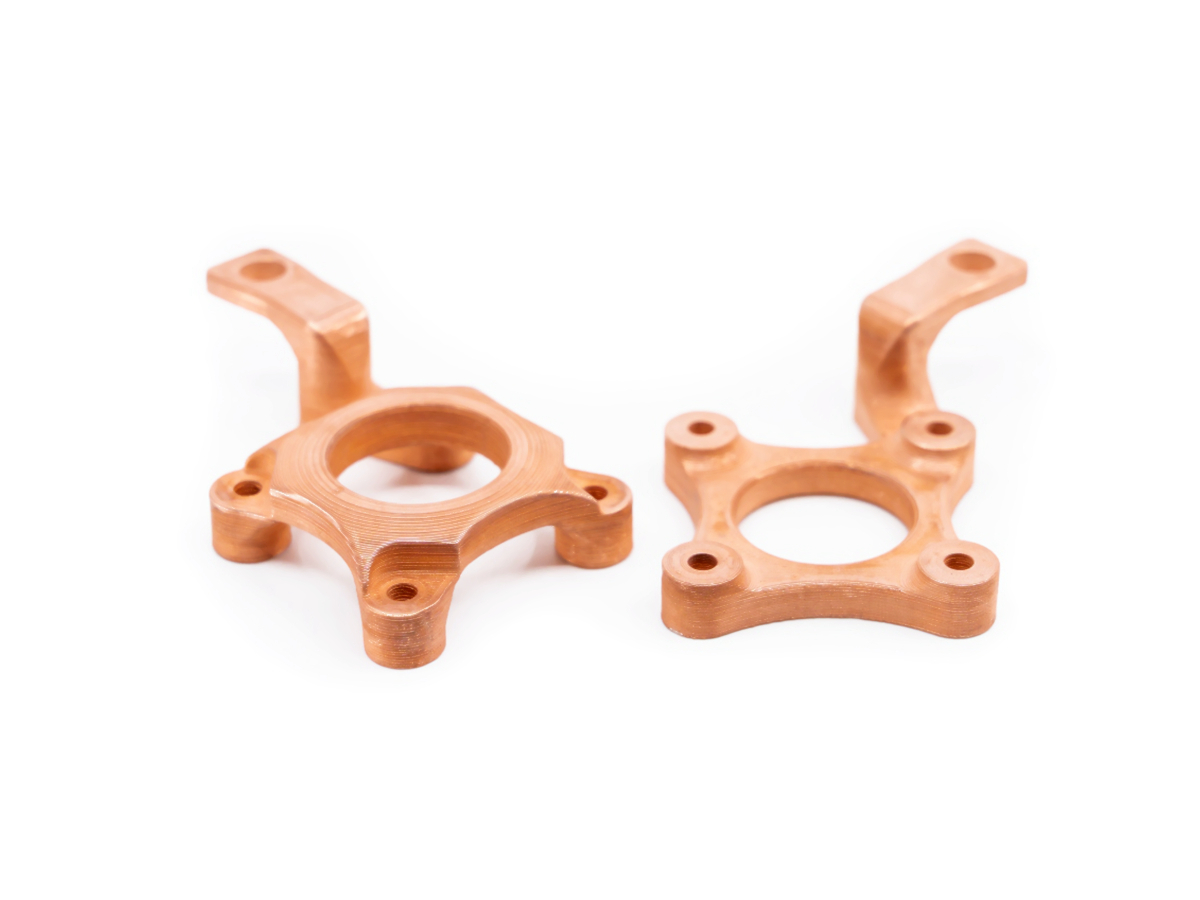
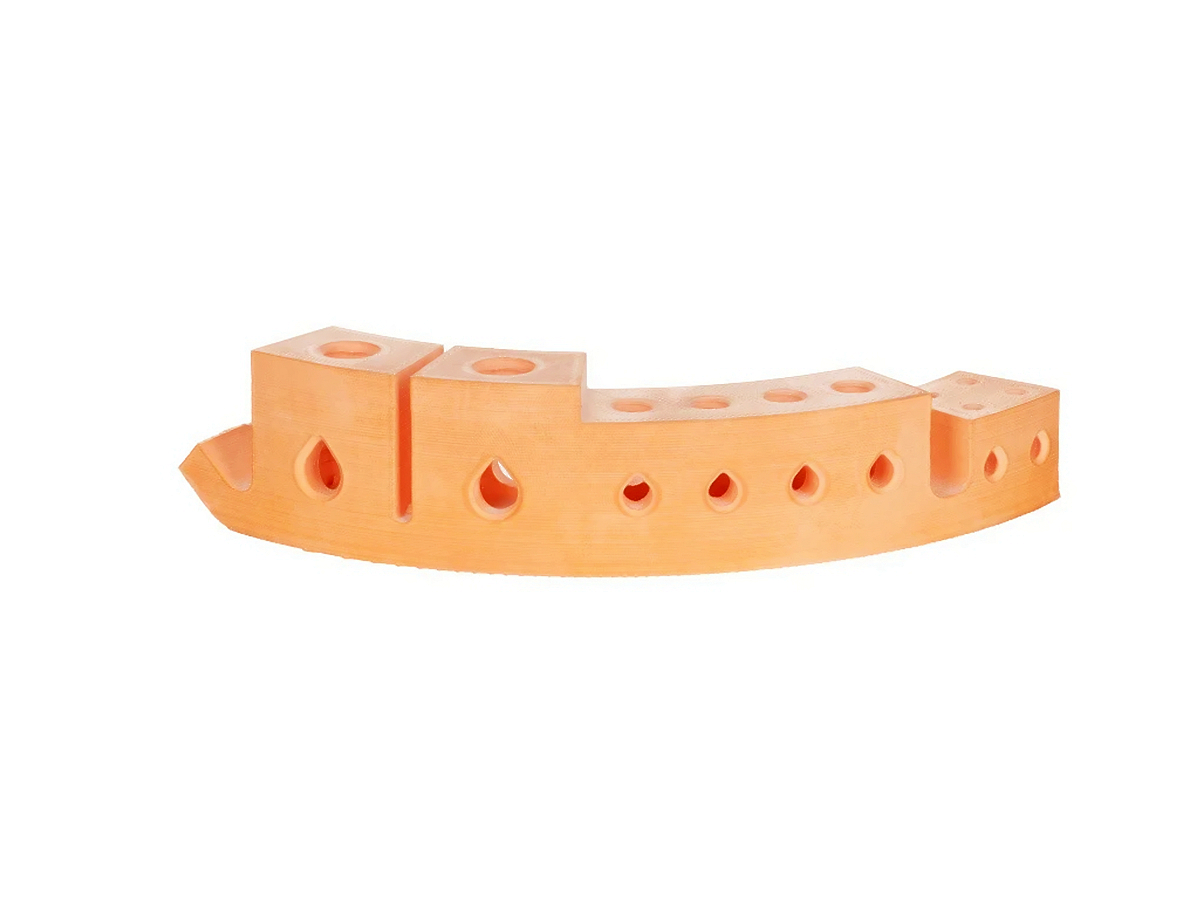
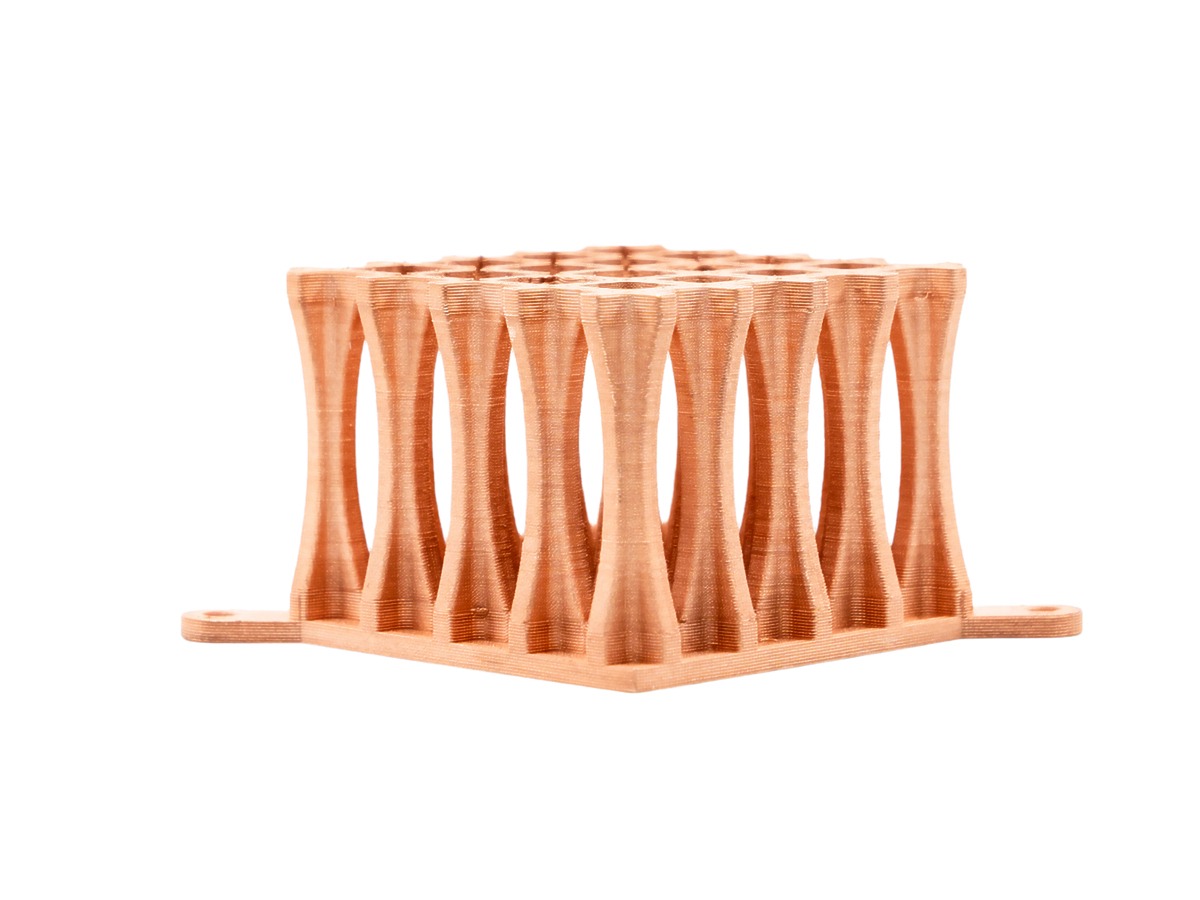
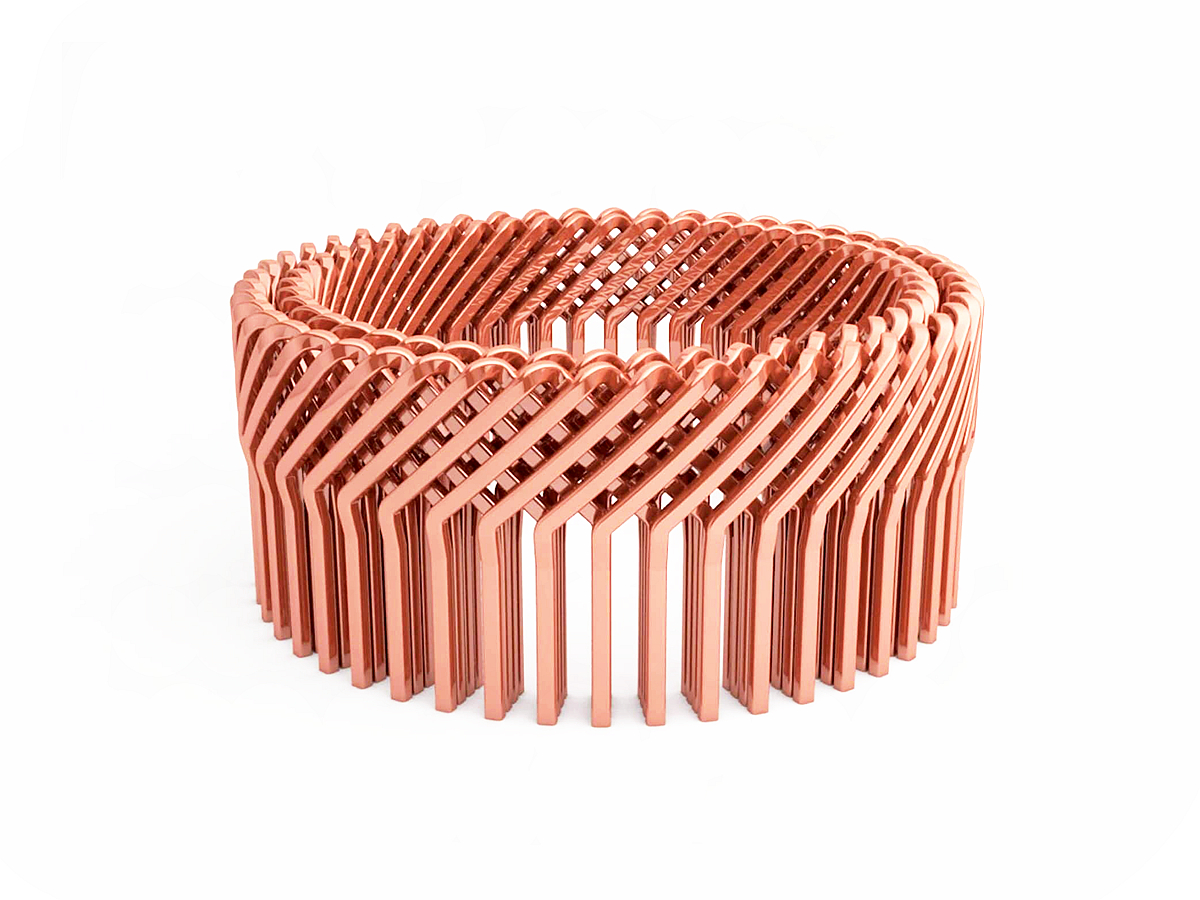
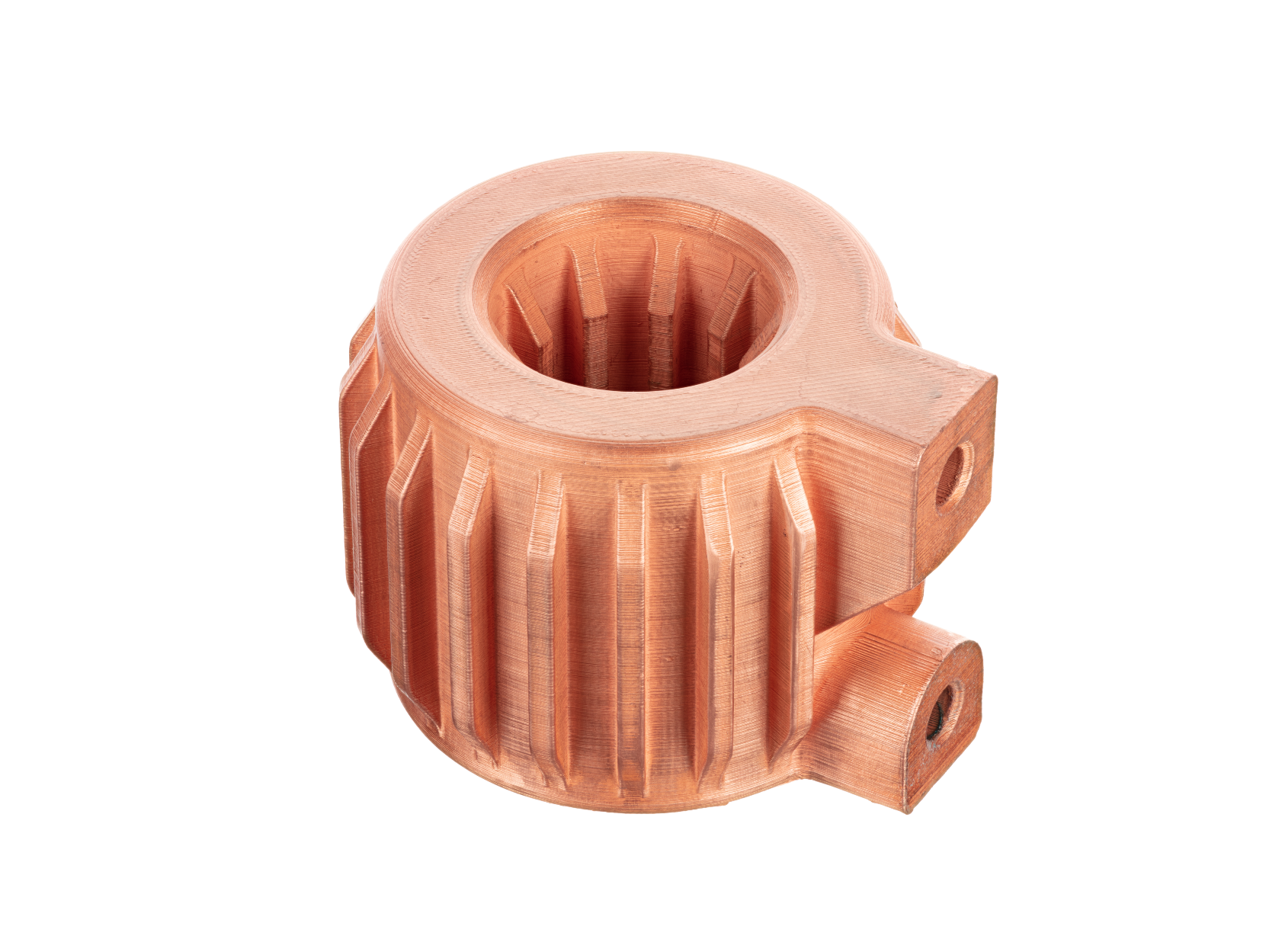
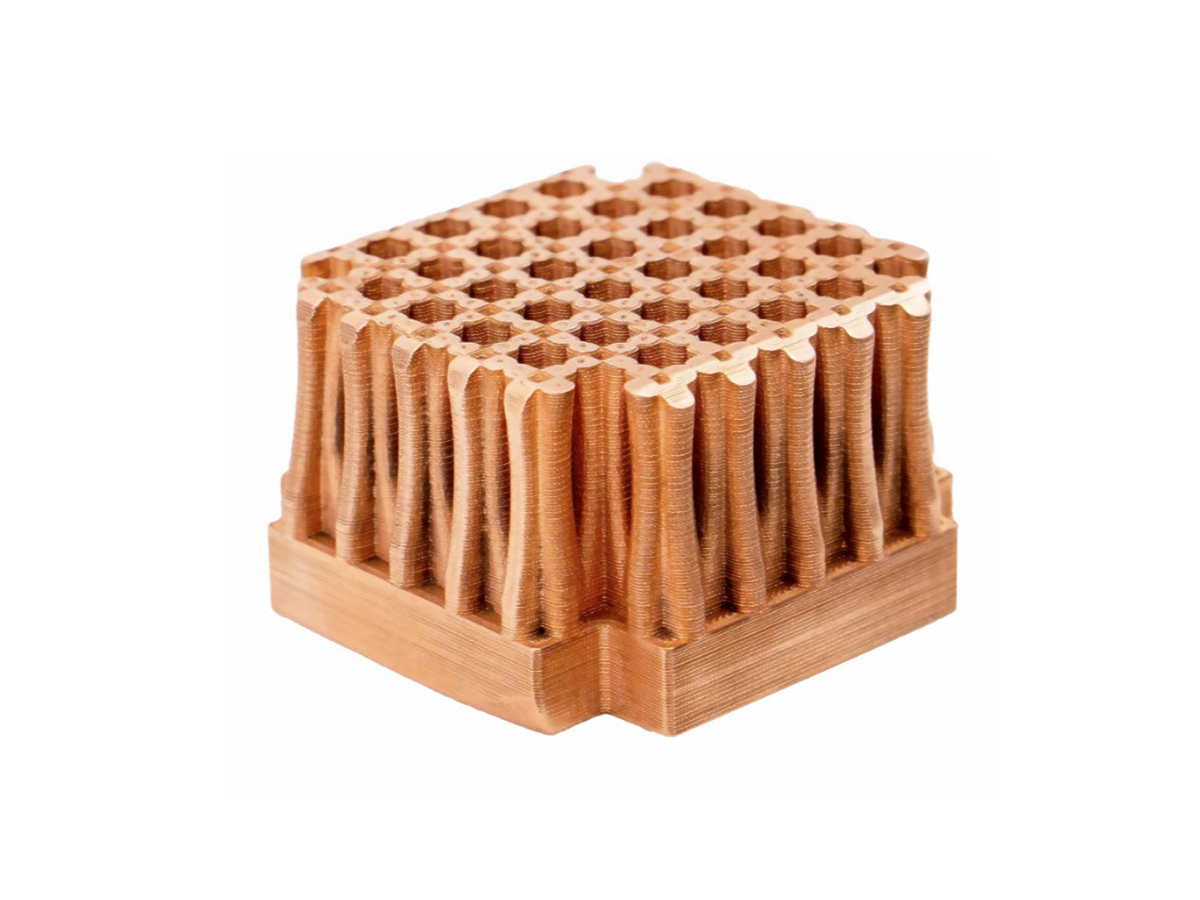
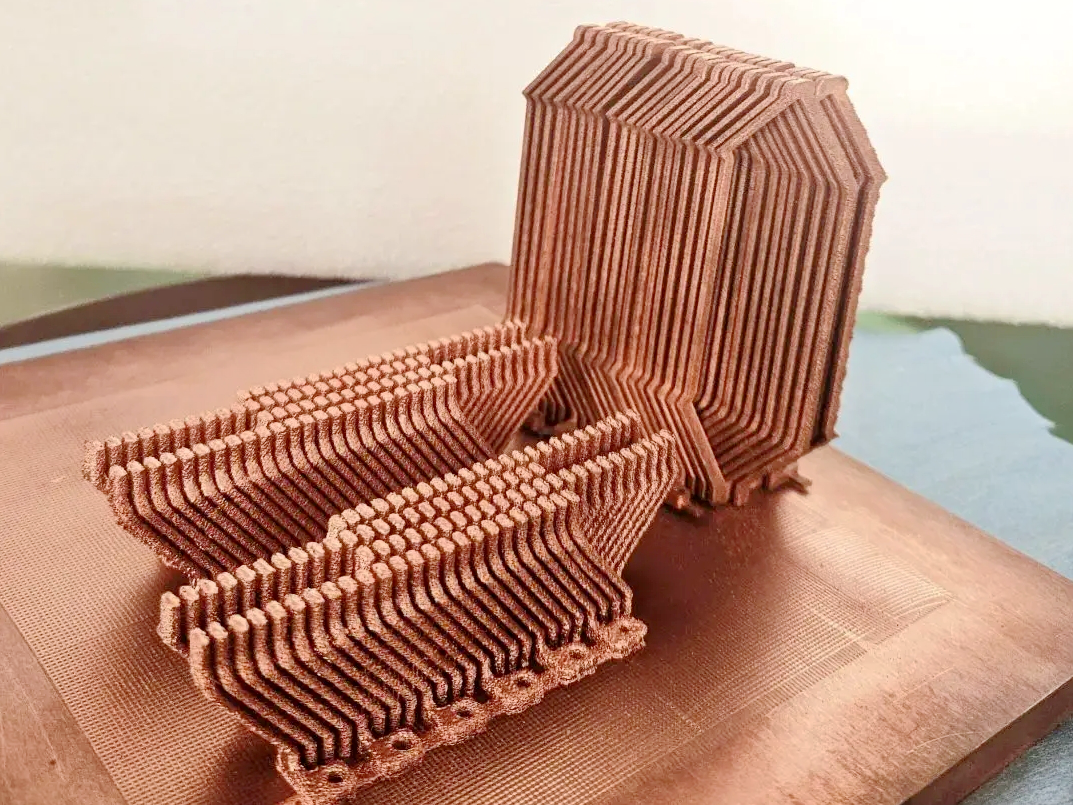
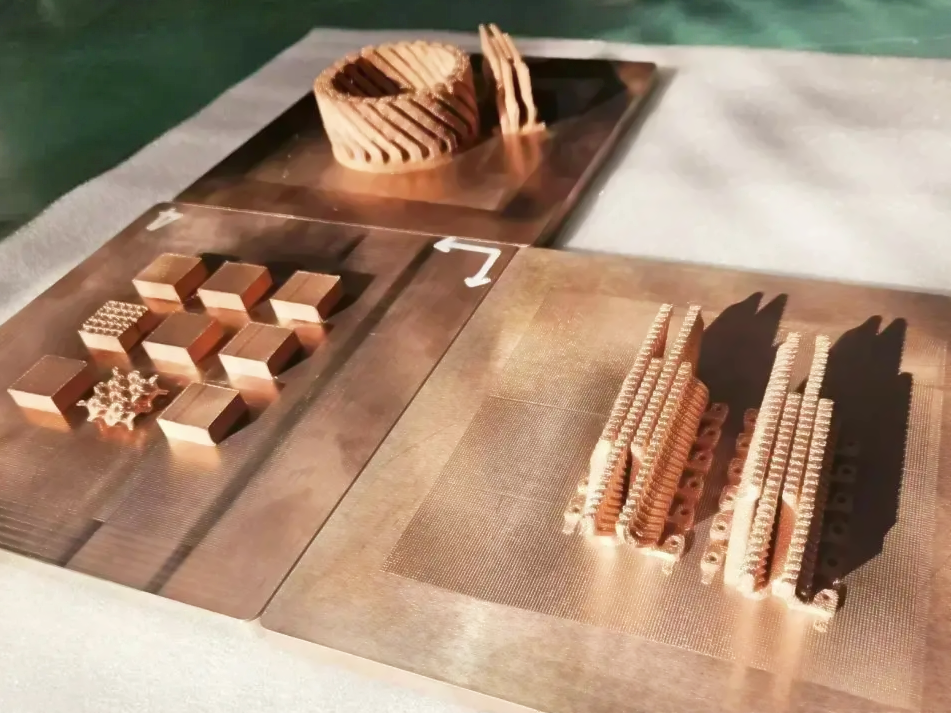
Copper 3D Printed Parts Gallery
Copper 3D printing revolutionizes industries with high-conductivity, precision-engineered components. From advanced cooling systems in aerospace to antimicrobial surgical tools in healthcare, our custom solutions enhance performance, efficiency, and durability. Experience rapid prototyping, superior heat dissipation, and innovative applications in electronics, automation, and energy with our cutting-edge copper 3D printing technology.
Let's Start A New Project Today
Copper 3D Printed Parts Design Considerations
Copper 3D printing presents unique challenges due to its high thermal conductivity and reflectivity. Effective design must address these properties to achieve successful prints with good electrical and thermal performance. Considerations include managing heat accumulation, optimizing geometries for thermal dissipation, and ensuring adequate surface finish.
Copper 3D Printed Parts Manufacturing Considerations
Copper 3D printing requires detailed attention due to its high thermal conductivity and reflectivity, which can affect laser absorption in powder bed fusion processes. Key manufacturing considerations include managing heat, ensuring consistent material properties, and optimizing post-processing to exploit copper's excellent electrical and thermal conductivities.